If you owe money on your student loans, you may be wondering what you can do to avoid getting behind on payments or paying on your loans longer than necessary.
One common solution to student loan debt is consolidation or refinancing — either to simplify your repayment plan, to save money on interest, or in some cases, both.
While student loan consolidation or refinancing won’t make your loans go away, there are plenty of tangible benefits.
Table of Contents
If you’re thinking of consolidating or refinancing your student loans, keep reading to learn more.
How to Consolidate Federal Student Loans
Most student borrowers take out federal student loans first, mainly because they come with low-interest rates and consumer protections like deferment, forbearance, and income-driven repayment plans.
And that’s why many borrowers don’t want to refinance with a private lender — they’re cautious about losing the benefits their federal student loans offer.
You can consolidate federal student loans without using a private lender.
Direct Consolidation Loan
A Direct Consolidation Loan, which is a type of federal student loan, allows you to consolidate several different federal loans into a new loan with one monthly payment.
There’s no cost for these loans, and you can complete the process online at studentaid.gov.
The biggest downside of Direct Consolidation Loans is that they won’t save you any money. They come up with your new interest rate by using a weighted average of your current rates, so the amount of interest you’ll pay stays the same overall.
Direct Consolidation Loans do let you extend the term of your repayment, however, which could be both a pro and a con.
If you want to keep federal benefits and consolidate so you only have one monthly payment to make, it’s likely your federal loans will qualify for this program.
The majority of federal student loans can be consolidated, including:
- Subsidized Federal Stafford Loans
- Federal Stafford Loans
- PLUS loans from the Federal Family Education Loan (FFEL) Program
- Supplemental Loans for Students
- Federal Perkins Loans
- Nursing Student Loans and Nurse Faculty Loans
- Health Education Assistance Loans
- Health Professions Student Loans
- Loans for Disadvantaged Students
- Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans
- FFEL Consolidation Loans and Direct Consolidation Loans (under a set of conditions)
- Federal Insured Student Loans
- Guaranteed Student Loans
- National Direct Student Loans
- National Defense Student Loans
- Parent Loans for Undergraduate Students
- Auxiliary Loans to Assist Students
Refinancing With a Private Lender
While Direct Consolidation Loans can help borrowers reduce the number of payments they’re making each month, the fact that they won’t save you money on interest means not everyone will bother.
If your goal is saving money on interest, you may want to consider refinancing your loans with a private student loan lender like College Ave Student Loans.
With a private lender, you may be able to refinance your loans with variable rates as low as 2.49%.
You can select a repayment period that works with your budget, provided you qualify.
Like Direct Consolidation Loans, refinancing with a private lender allows you to lump all your current student loan payments into one single loan with one monthly payment, and hopefully save you money in your monthly budget, over the life of your loan, or in some cases both.
You can use the College Ave Student Loans Refinance Calculator to learn how you can save.
Consolidating Student Loans — Pros and Cons
If you’re on the fence about consolidating student loans with a Direct Consolidation Loan or refinancing with a private lender, it helps to think over all the potential downsides as well as anything you might gain.
Here are some of the main advantages and disadvantages to mull over:
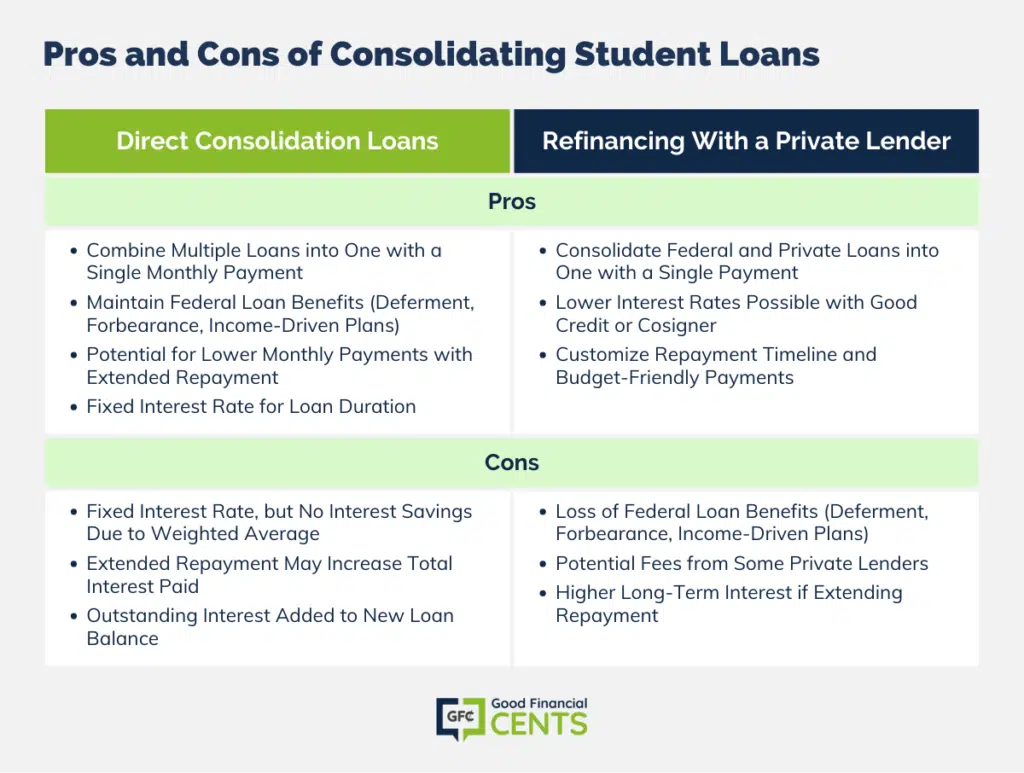
Pros of Direct Consolidation Loans
- You get the benefit of combining several new loans into one new one that only requires one monthly payment.
- You get to maintain the federal status of your student loans, which includes access to benefits including deferment, forbearance, and income-driven repayment plans.
- You may qualify for a lower monthly payment that works better for your budget if you extend your repayment timeline.
- Direct Consolidation Loans come with a fixed interest rate that will never change.
Cons of Direct Consolidation Loans
- While you will get a fixed interest rate, the fact these loans use a weighted average of your current rates means you won’t save money on interest.
- Extending your repayment timeline could mean having to pay more interest over time.
- Any interest that’s outstanding on your original loans will get added to your new loan balance, which means that “interest may accrue on a higher principal balance than might have been the case if you had not consolidated,” according to the U.S. Department of Education.
Pros of Refinancing With a Private Lender
- You can combine all your existing federal and private loans into a new private loan with one monthly payment.
- You may be able to secure a much lower interest rate if you have great credit or a qualified cosigner.
- You can typically choose your repayment timeline and tailor your payments to fit your budget and your lifestyle.
Cons of Refinancing With a Private Lender
- When you refinance federal student loans with a private lender, you lose out on benefits like deferment, forbearance, and income-driven repayment.
- Some private student loans come with fees you’ll want to be aware of, although many don’t charge any application fees or origination fees, such as College Ave Student Loans.
- You may pay more interest over the long run if you extend your loan repayment period.
The Bottom Line
Consolidating or refinancing student loans can help you in more than one way. Not only can consolidation or refinancing give you one monthly payment to pay each month instead of several, but you may be able to choose a new monthly payment that fits with your budget.
If you opt to refinance with a private lender, you may even be able to save thousands of dollars on interest payments over the years.
Before you move forward with consolidation or refinancing, however, it helps to ask yourself some important questions. For example:
- What do you hope to gain from consolidating or refinancing your loans?
- Do you have federal loan benefits you need to protect?
- Do you have great credit that could help you qualify for a low interest rate with a private lender?
- If not, do you have a family member with great credit that’s willing to cosign?
By asking yourself these questions, you put yourself in the best position to benefit from whatever option you decide on — even if that means doing nothing and sticking with the loans you have.







